A Comprehensive Review of Agile vs Waterfall Methodology
December 4, 2025
12 min read


Agile vs Waterfall Methodology: Understanding the Key Differences for Project Management Success
Choosing between agile and waterfall methodologies might be the most consequential decision you make when starting a project. Get it wrong, and you'll spend months fighting against a methodology that doesn't fit your reality—rigid planning when you need flexibility, or chaotic iteration when you need predictability. Both waterfall project management and agile project management have their place, but they're fundamentally different approaches to project management that suit different situations. The problem? Most teams pick based on what's trendy or what they've always done, not on which methodology actually matches their project's characteristics and constraints.
By understanding the core key differences—from how each handles project requirements to their approach to risk management—you'll be equipped to make the right choice when choosing between agile and waterfall for your next software development project.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Project Management Methodologies
Waterfall: The waterfall methodology is a sequential project methodology that requires fixed project requirements early in the project lifecycle, delivering the entire project at the end of the project. It is best for simple projects with stable scope.
Agile: Agile is an iterative methodology that embraces change and continuous feedback. Agile projects break down the project project into smaller iterations (sprints), delivering functional software frequently throughout the entire project lifecycle.
Key Differences: Waterfall is linear and rigid; agile is circular and flexible. Waterfall manages change poorly; agile encourages change and adaptation through feedback throughout the project.
Risk Management: Waterfall attempts to manage all risk at the beginning of the project, whereas agile provides continuous risk management by exposing issues early in the project lifecycle through frequent delivery.
Team Structure: Waterfall has hierarchical, siloed team member roles; agile teams are self-organizing, cross-functional, and highly collaborative.
The Hybrid Solution: Choosing between agile or waterfall is not always necessary. A hybrid project management methodology combines the control of waterfall for planning with the flexibility of agile for software development and project execution.
What is the Waterfall Methodology and How Does it Structure the Project Lifecycle?
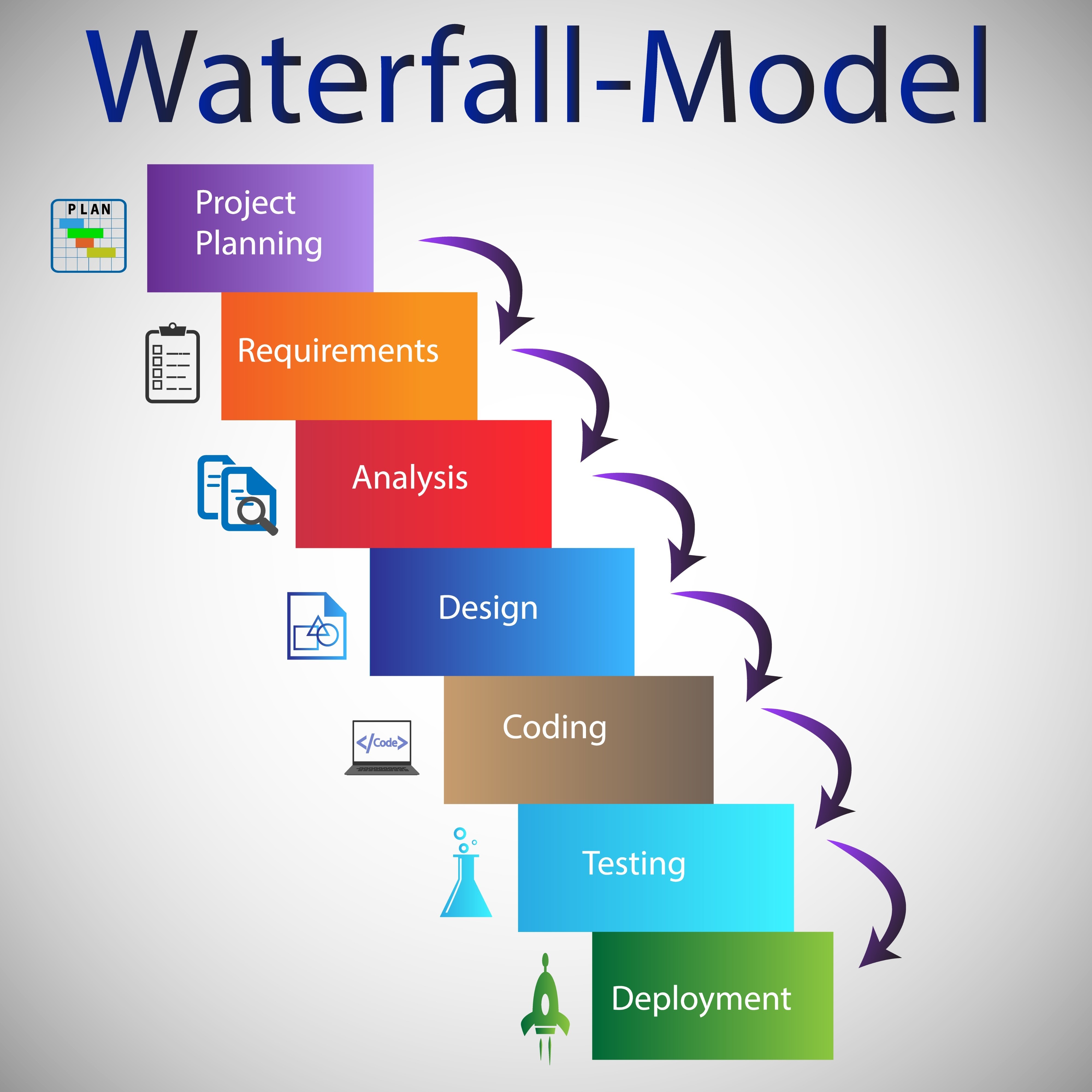
The waterfall methodology is one of the oldest and most widely recognized project management methodologies. It is a sequential project methodology where progress flows steadily downwards, like a waterfall, through pre-defined phases. These phases—typically Requirements, Design, Implementation, Testing, and Deployment—are strictly sequential. The next project phase cannot begin until the previous one is entirely completed and signed off.
The waterfall approach requires all project requirements to be meticulously gathered and documented early in the project lifecycle, ideally before any design or coding begins. This results in a comprehensive project plan that maps out the entire project timeline and project lifecycle from start to finish. The strict nature of waterfall means that changes to the project scope or project requirements after the initial phase are difficult, costly, and disruptive, often requiring the project manager to return to earlier phases.
The strength of the waterfall methodology lies in its simplicity and reliance on a structured approach to project management. For highly regulated industries or projects where the scope and technology are perfectly understood and will not change, the waterfall model offers clear documentation and easy progress tracking. The structure dictates a clear handover from one team member or department to the next.
What Defines Agile Project Management and How Does it Differ from Traditional Project Management?
Agile project management is an iterative approach to project management that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. Unlike the linear structure of waterfall, the agile approach breaks down the project project into smaller, manageable time periods called sprints or iterations. At the end of each iteration, a functional piece of the product is delivered, allowing the client to provide feedback throughout the project.
The core difference between agile and waterfall lies in their approach to change and planning. Agile planning is continuous; the project requirements are refined and re-prioritized before each sprint, allowing the development team to respond quickly to market changes or evolving project requirements. Agile methodologies like Scrum are built on the agile principles of continuous delivery and self-organizing agile teams. The agile process is defined by its ability to adapt. Agile allows teams to continuously learn and improve the product based on real user feedback, delivering value much faster than the single, large delivery that marks the end of the project in waterfall development.
What are the Key Differences Between Agile and Waterfall Methodologies?
The key differences between the waterfall and agile methodologies can be summarized across three main categories: planning, execution, and change management. Waterfall is linear and prescriptive; the project plan is defined at the beginning of the project, and execution is strictly sequential, where a project phase must be complete before the next begins. Agile is an iterative methodology that focuses on continuous planning and execution in short cycles.
In terms of execution, waterfall focuses on delivering the entire project as one final product at the end of the project lifecycle. In contrast, agile focuses on breaking down the project project into smaller functional pieces, delivering valuable features continuously to the client throughout the project.
Finally, their approach to change is fundamentally different. Waterfall treats change as a disruption to be avoided, requiring formal change requests that can delay the project timeline. Agile encourages and welcomes change; agile methodologies are specifically designed to incorporate new or altered project requirements quickly and efficiently into the next iteration without derailing the entire project timeline.
How Does Risk Management Vary Between the Waterfall and Agile Approach to Project?
Risk management varies significantly depending on the project management approach. In the waterfall methodology, the primary strategy for risk management is extensive planning early in the project lifecycle. The detailed project plan attempts to identify and mitigate all potential risks and uncertainties at the beginning of the project, aiming for a predictable and controlled execution phase.
However, the major weakness of waterfall risk management is that risks are often not truly realized or addressed until late in the project, during the testing phase. If a fundamental flaw is found, or if the original project requirements are discovered to be wrong, fixing it requires substantial rework of multiple project phases, significantly increasing the cost and potential failure of the entire project.
Agile project management takes a fundamentally different approach to project risk management. Agile allows risks to be managed continuously and incrementally. By delivering functional software every few weeks, agile teams receive immediate validation, identifying and mitigating technical or functional risks much earlier. This iterative approach means problems are smaller, cheaper, and faster to fix, providing a more robust and responsive form of risk management.
How Do Project Requirements and Scope Change in Waterfall vs. Agile Projects?
The handling of project requirements and project scope is perhaps the clearest distinction when you compare agile and waterfall. In waterfall projects, the project requirements are fixed and frozen after the initial project phase. The success of the waterfall method relies on maintaining a rigid project scope, and any significant changes are viewed as scope creep and must be managed via formal, bureaucratic change control processes.
In agile projects, the project requirements are fluid and emergent. While the high-level project scope (the vision) is defined, the detailed features and their priorities are continuously reviewed and adjusted throughout the project lifecycle. Agile planning allows the client to introduce new project requirements or change existing ones, which the agile teams will incorporate into the next sprint.
This flexibility makes agile is ideal for projects where project requirements are likely to change due to market conditions or user feedback. Agile allows teams to adapt the product iteratively. In essence, waterfall aims to deliver the solution as defined at the beginning of the project, while agile aims to deliver the solution that provides the most value at the end of the project.
In What Scenarios is the Waterfall Method Best Suited for Project Success?
While waterfall has fallen out of favor for much of software development, it remains the most appropriate methodology for specific types of waterfall projects. Waterfall is best suited when project requirements are highly stable, well-understood, and unlikely to change. This is often the case in regulated industries where documentation and pre-approval are critical, such as certain government contracts or medical device manufacturing.
The structure of the waterfall methodology provides predictability that can be vital for certain project management needs. When the technology is mature, the design is simple, and the final outcome is clear, using waterfall can provide a structured approach that makes tracking progress against the project plan straightforward. The strict handovers between project phases and clear documentation are beneficial when compliance or external audits are mandatory.
When is the Agile Approach Best for Project Execution and Development Process?
Agile is often the best choice for project execution and the development process when dealing with complexity, uncertainty, and a need for speed. Agile is ideal for innovative software development, mobile app development, and any project where the end-users' needs are not fully known at the beginning of the project. The nature of agile makes it perfect for adapting to market feedback.
The agile approach shines in environments where the value of feedback throughout the project is recognized. By breaking down the project project into smaller iterations, agile development enables the development team to get a functional product into the hands of users early. This helps mitigate the risk of building software that nobody needs, which is a common failure point for long waterfall development cycles.
What is the Difference Between Agile and Waterfall Project Management in Team Structure?
The core difference between agile and waterfall project management is reflected in their team member structure and roles. In waterfall project management, the structure is often hierarchical and siloed. Each team member or department (e.g., analysts, designers, coders, testers) typically completes their work and passes it down to the next group in the sequential project flow. The project manager acts as the central point of control, directing the entire operation.
In contrast, agile methodologies rely on small, cross-functional, and self-organizing agile teams. These agile teams typically contain all the skills necessary to complete a project into smaller chunks from start to finish. The role of the project manager is often replaced by a Scrum Master or Agile Coach, who acts as a facilitator, clearing obstacles for the team members rather than giving strict directives.
How Does Project Management Tool Selection Impact Both Waterfall and Agile Methodologies?
The choice of a project management system or tool must align with the chosen methodology. For waterfall, the ideal tools are those that facilitate strict chronological planning, dependency mapping, and comprehensive documentation. Tools for waterfall emphasize creating detailed Gantt charts and tracking progress against the fixed project timeline and original project budgets.
For agile methodologies, the tools must support an iterative approach and continuous flow of work. Agile tools focus on visual management (e.g., Kanban boards), backlog management, sprint planning, and facilitating continuous communication. They emphasize real-time feedback and metrics like velocity. Project management processes in agile rely on tools that make agile planning and re-prioritization simple and visible to every team member.
Using the wrong tool for the methodology can undermine effective project management. For example, trying to manage an agile project with a rigid, waterfall-centric tool will stifle the necessary flexibility and continuous communication. Conversely, using a highly flexible agile method tool for a contractually fixed waterfall project could compromise the necessary documentation and strict control.
Choosing Between Agile or Waterfall: How Can a Hybrid Project Management Approach Offer the Best of Both?
When faced with choosing between agile or waterfall, many organizations are now turning to a hybrid project management approach. This approach recognizes that the complexity of modern project management often requires combining the strengths of both waterfall and agile methodologies. For instance, a project lifecycle might start with a waterfall-style phase for initial requirement gathering and regulatory approval (where documentation must be fixed).
Once the high-level project requirements and architecture are defined, the project execution shifts to an agile development process. This allows the core development team to use the speed and flexibility of the agile approach for software development, while still maintaining a rigid, documented base. This blending of waterfall and agile software development is often called a "Wagile" approach.
The key to a successful hybrid project management methodology is knowing which elements of waterfall (control, upfront planning) and agile (flexibility, feedback throughout the project) to apply to different aspects of the project. By combining the structured approach of waterfall with the iterative approach of agile, organizations can maximize project success by mitigating risk where needed and maximizing adaptability where possible.
Find Your Next Talent
Hire South Africans in Days not Weeks, and only pay after 4 weeks
Or schedule a call with Bojan.


